Warning
- Contains Explicit Language
- Use as a fun way to learn, this is intended for personal use and not shared with the Academic mentality in mind
- Covers the lecture 1, lecture 2
Understanding of Computers and its behaviour.
Let’s think of something. anything. did you think of something? no? Yes? If you did, good job. continue thinking about it. if you didn’t that’s okay. Let me help you out. Lets think of a cat. Orange. and fluffy. Like a cloud. Hmm, why don’t we name them Master Willium Fluffles Esquire the third. Mr. Fluffles for short. Now isn’t he cute?
Pat yourself on the back for imagining a chubby cute cat. Good job.
By the way, wanna hear a secret? You, just thought and acted as a computer. Interesting isn’t it? The people in the back would now be asking, what I meant by that. Allow me.
Keep the cat in mind and lets go on a short adventure. What adventure? An adventure to find out what a computer is. Oooh, fancy.
Hmm, you find a old wizard, wearing gray robes and red hat, completely ridiculous if you ask me. You ask him. “Mr, what is a computer?” He says. “Dude, Im a wizard, you’d have to check with the IT department for that.” Well that didn’t work out. Don’t worry about the IT department. I am the IT department.
So; Looking at a computer, at a glance. What can you make out? Is it the plastic case, that has weird hardware and spinning fans or is it the screen that spews out the images and occasional blue screens at the worst time possible? The answer is yes. Well that’s… what you expected, you’re not a kid that needs to be taught what a computer is.
But; under the hood, under the plastic covers of the components and crazy RGB’s, what does a computer do exactly? I’m glad you asked. Apparently, A computer
- Stores large amounts of data. (Obviously, I mean I have 300 gigs worth of Games, (I know I need a better hobby.))
- Process a large amount of Data
- So, You know how a game work right? A game has multiple game files, scripts, textures and music (data) that when the game is played all of these files are processed for the game to come ✨alive ✨. So a computer can process a Copius amount of data. (I mean, NASA computers? psh)
- Protects data and resources (I hope this is kind of self explanatory, ever guessed why you put a password in your computer?)
- Data Analysis. (Nasa? I mean they do get data from satellites after all)
- Enables communication
- Networking (Don’t even wanna talk about it actually. but you know, connecting to the internet, IP blah blah, you get the gist)
That’s a computer? You may ask. No my sweet summer child. That’s the Functions of a computer. I mean if you think about it, we literally gaslighted a rock into thinking. That’s what a computer is.
Ahem, allow me to give you a little bit of ✨More ✨
What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos.
So how the fuck, did we make a rock think? Don’t ask me, it involved alot of electricity apparently. But that’s not the point. The point is. How does a computer do what it does?
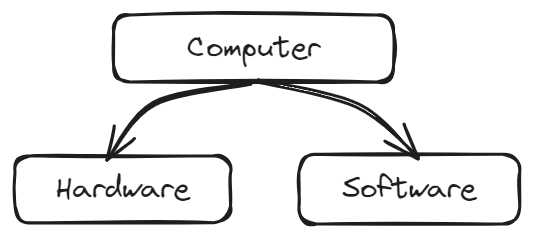
Hardware and Software
Well, for that we have to think, what makes a computer. Right? You know it. I know it. What you see and touch— In the computer. Those physical components are what we call ✨ Hardware ✨.
Hardware is your arms and legs right? so, how do you go about moving your arm to the left? Easy you just move your arm to the left. Well; true. But like, How does that process work?
Well first your brain comes to an executive decision that it will move the arm to the left and not right. Then your brain sends the instruction through your neurons to the appropriate muscles. And your muscles carry out the job. and viola, your arm is now turned to the left.
Just like that; a computer has a brain. CPU, ring any bells? good. But unlike our brain, which comes with their own BS, a CPU doesn’t. Why you ask? because its a machine. So, what is necessary ingredient of a machine? telling it what to do. so that telling part is done by a little something called ✨ Software ✨
What is Hardware?
Hardware is any part of your computer that has a physical structure, such as the keyboard or mouse. It also includes all of the computer’s internal parts.
Software: What is it?
Okay, So Software is the thing that tells the computer to do something, cool. Now what? Well, We have to understand why is Software, you know. So; according to someone who I know that knows someone who knows someone who said this.
you can think of a software as a computer program that provides a set of instructions to execute according to its user’s commands and tell the computer what to do.
What is Software?
Software is any set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do and how to do it. Examples of software include web browsers, games, and word processors

Note
A software includes instructions for a computer to produce a specific result, and acts as a bridge between the user and the computer’s hardware to perform tasks, solve problems and modify data.
HmMMmm. Yep. That tracks. So, remember the cat we imagined earlier? I was the software. Instructing you. to do something. that resulted in a specific result. ← The imagination of our glorious Mr. Fluffy. Get it now?
Btw say Hi to Mr. Fluffy.

Now that we basked in glory of Mr. Fluffy. What makes a Software?
Software: Programming and Programmer.
According to something, I’m sure. The process of writing a software is called: ✨Programming ✨. It’s fun they said, try it out they said; they were wrong. And the unfortunate soul that does this Programming, is called a: ✨Programmer ✨ Well done in naming sense, 10/10 for creativity. And here’s another. The instructions the programmer write are written in something called: ✨Programming Language ✨ Bravo. What a genius, I wonder who came up with the names.
3Ps
The process of writing is called Programming, and is written in a Programming Language by a Programmer
Well what is this programming language you speak? patience my child, I’ll get to it when I get to it. which is eventually.
In the meantime, Since you have chosen to become a poor soul who stares at a computer and write a cryptic alien language (dramatic much) to become a computer Shakespeare to Idk, something. lost the sentence after a while. The point is. You wanted to become a programmer, guess what chief. You gotta know how to make a software. Who would’ve thought.
Software Development Lifecycle.
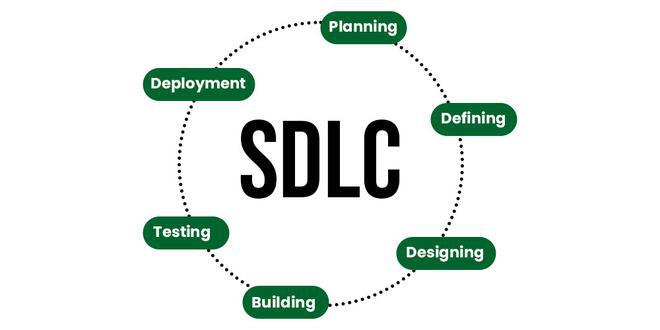
So according to trust me bro. The process of creating a Software is called Software Development, Yeah. Right. Sure. So, that means, you got to develop it. Great English there buddy. To build a software, you have to know what’s called a ✨Software Development Lifecycle ✨ Which is a fancy sentence used to describe the steps of software development, Why is it called a lifecycle? because at the end it crashes and burns. I’m kidding, that only happens when Steve’s around. I’ll tell you about him later. No, It’s called a lifecycle is because, It repeats. Like a circle. You get what I mean. So what are these steps? Glad you asked. They are:
- Analysis
- Planning
- Defining
- Building
- Testing
- Deployment.
Alright, So what does any of these mean. Well cupcake, imagine this. I’m a client. Who comes to you to ask you to create me a website. Alright. Now what is your job? Creating that website for me. How do you do it. If your first question is not what kind of website, go drink some water. If it is. Good job, also drink some water you dehydrated camel in denial. Anyways, Why would you ask such a question? Right. To understand what is my requirements are. Then you will Plan and Define what are my goals are for the website. Once you have the overall idea, you will go about Designing the website and how it needs to be build. Once that is over, you’ll actually code it right?, that is Building. Once you build it, you’re not going to push it to the prod, and say “No tests needed, we die like men”. No no no, we do a little bit of Testing, squish out some bugs, iron out some wrinkles. And then, we Deploy it to the web.
Oooh, congratulations, you’ve finished one cycle. Now come the fun part. A project is never over, it just goes into a long hiatus. So why is this a lifecycle? Because, the website needs an update, it needs a new feature; So? what do you do? You figure out what is this new feature, you plan it, you define it, you design it and then you build it, after testing you deploy it. And rinse and repeat.
 (don’t think much of the points in each, you’ll get to know them later, if you want to search them up just search Software Processing Models.)
(don’t think much of the points in each, you’ll get to know them later, if you want to search them up just search Software Processing Models.)
What is Software development lifecycle
The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is a systematic approach to producing high-quality software. It outlines a series of phases that software development teams follow to create, test, deploy, and maintain software applications
Software: Step by Step.
Now you know what is the Software Development Lifecycle is right? Now is the fun part. Using it.
Okay. Remember that wizard with the grey robes and red hat? Guess what. He comes to you one day and asks you to do him a favor. He’s bad at math. Somehow he’s a wizard. Idk ask him. So, he says to you. To create a Software to add two numbers together. Easy. just add one number to the other. Right? well hold your horses. It’s not that easy telling that to a computer.
First step first.
Analysis and Defining of the Problem
Well, before we dive in we have to understand the basics of the spell we are going to cast. (what am I even doing) We are going to learn about the IPO model. The input, the process and the output. Okayyy? What is that? Well, The IPO, input, process and output is what the computer software does using the computer. It takes some stuff (inputs), does some stuff to it (process), and throws what happens out (output). Now you know.

Just kidding,
Input
Input is the process of entering data or information into a computer system using input devices such as a keyboard, mouse, or scanner. The input data can be in the form of text, numbers, images, or any other type of information that needs to be recorded in a digital format
Process
Process refers to the operations performed by the computer to manipulate or analyze the input data. This includes executing software applications, performing calculations, sorting and filtering data, and running programs.
Output
Output refers to the result of the processed data that is presented to the user in a usable format. This can be in the form of text, images, graphs, charts, or any other format that is meaningful to the user
Peachy? Good. Now the fun part.
In the analyzing stage, You have to identify clearly what are the inputs of the program, what process is done to it to get the result and what will become the output.
So; with that lets go back to our hippie wizard.
His goal is to create a software that adds two numbers together.
Allow me to show you some magic.
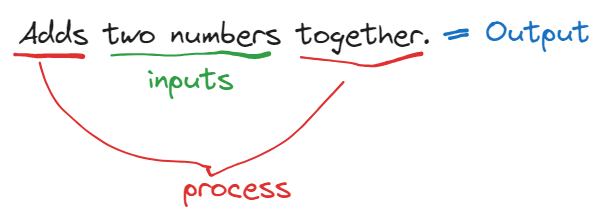
Okay, How the heck did I get that? wouldn’t you like to know weather boy.
Listen up buttercups. First. Figure out what is being provided to you, what are the required data to solve the problem. That is your input. Second. Figure out what needs to be done to the said data to turn it to the required result/outcome. Congrats you have the process. The third is the result of that process.

Lets look at this one. It says there was an experiment, blah blah blah and we have given the remaining 3 people’s heights and the calculated average. See how those two are required for us to go forward? Those are our input. What we have to find is the missing height. Which is the output, because that’s what we get after we fiddle with the inputs no? So what is find? that is our process. The process of finding the output from the input.
Let’s break it down step by step:
- Given:
- Let the known heights be , and .
- Let the two missing heights be and.
- The average height of all five people is given as .
- Calculate the total height: Since the average height is given, we can compute the total height of all five people:
- Sum of known heights:
- Calculate the sum of the missing heights: The sum of the two missing heights is the total height minus the sum of the known heights:
- Estimate missing heights: Since the two missing heights are almost the same, let’s assume: This means that: Therefore, the missing heights can be approximated as: See how we figured that out? Good. Now the next part.
Designing
Now designing is, well, designing a computer program to achieve what we figured out earlier. Like turning the text idea, into a rough code, computer program. Or something along the line. According to the slides, it means creating an algorithm to achieve the process and output.
Designing
Use algorithms to prepare a solution
- Algorithm: A step-by-step set of instructions designed to solve a particular problem.
- The key characteristics of an algorithm
- State instructions precisely, without ambiguity
- State instructions in order
For this; we use a little something called ✨Pseudocode ✨
Pseudocode
What is this sudo something something? Do you know whats the meaning of “pseudo”? If you know the meaning of that word, you’ll get what I’m trying to tell you. So the word, “Pseudo” means something, fake, pretending to be the real thing Okay? What does that picture us? Lets rethink, Pseudocode; pseudo + code. So that means, whatever we are writing as “pseudocode”, is FAKE and is pretending to be Actual code.
Alright? Why do we need this fake code then? we are genuine programmers right? Well my sweet summer child. Just six months ago, you didn’t know what Java was, did you? if you did, pretend you didn’t now, picture me this.
You come to me, as a client, or a designer who had this brilliant idea for an app and you want to convey that idea to me, the programmer, how you want to code it. Instead of going about it and yapping about it for hours, would’t it make it easier for you to write down the functionality of it like a code and show it to me? for example, lets say you had an idea for an app that took in a number and returns if its an odd or an even number? so how do you explain that to me? Well, you could simply write it as a fake code to me, this doesnt have any syntax, or compiling or anything that sort of. simply put there are no rules, you can write it as however you wish it to be written.
So for an example lets take the above program and turn it into a pseudocode.
- First, write down what you expect to happen.
This program will allow to check
Whether the number is an even or an odd number- Write down it a bit more detailed, like the decisions, conditions, if elses and loops to better show the decision making and execution mechanism
if "1"
print respons
"Odd number"
if "2"
print response
"Even number"Now, does that make sense? kind of? does it have any syntax, language rules? absolutely not is that the way we were taught? nope So how do we write it the way we were taught?
FOR THAT remember earlier, where we identified the IPO model? great so, first we have to figure out the IPO of this program. Lets write it
- Input:
- What do we require for the output?
- We need the number to determine whether its even or odd right?
- so that’s our input.
- Process:
- Well, how do we find whether its an even or an odd number?
- Let’s do an experiment.
- Tell me whether 10 is even or odd.
- Just by looking at it you know its an even number right?
- alright, but, your brain, how did it figure it out?
- Lets put our brain into slow motion and go step by step.
- first we saw the number,
- we saw it was 0 at the end
- we know that any number that ends with a multiplier by 2 or 0 is divided by 2 with no remainders.
- So, we know that 10 is divisible by 2 with no remainders making it an even number.
- OR you could’ve thought, 10 is a multiplier of 2, 2 ⨉ 5 so it means its even right?
- Even then, you find that out by 10 / 2, and finding there are no remainders.
- Okay, so that’s our process.
- Whatever number we have, we have to divide it by 2 to see if there are any remainders, if there is, then the number is odd, otherwise its even.
- I want you to pay close attention to these keywords in any problem. “if”, ”Else’,’ “equals”, “greater / less than”, “or”, “and” These are your conditions.
- Now that we have the process lets just write it out.
- Output: if its even or odd.
Okay. lets write it, SLIIT style. Step numero uno (french for one I think)
- Since we are faking a java program we gotta tell who ever is watching that this is for a java program.
- I don’t think there’s much to think about it,
- you just write start and end.
- You know how java programs have
public static void main(...)? - we are telling them that we are inside this
mainfunction. - Thus
BEGIN MAIN
...
END MAINwe got that? Just hang in there
Step number two.
- Now, we have to define, like explicitly tell what are our inputs are.
- you know what define means? it means give a meaning to.
- so; we have to give a meaning to our inputs, that is rock solid throughout the program.
- These are also our inputs and could be Variables within our program.
BEGIN MAIN
DEFINE number AS TYPE_OF_VARIABLE <- (I'll explain later. Focus on Define).
END MAINSo above, we have defined a number, as a type of variable. Now variable types are explained later, but you know there are integers, strings, chars, doubles, floats right? so what we do here is explicitly telling the reader, that look, this number? we need it to be this type of variable right at the top of the program.
Now comes the step three.
- We are going to write step by step, the functionality
BEGIN MAIN
DEFINE number AS INTEGER
INPUT number <- saying that we are taking input!
IF number % 2 == 0
PRINT "Even"
ELSE
PRINT "Odd"
END IF
END MAINdo we have an understanding? Look, there’s nothing much to worry about here. At this point in time, we have a good understanding of what a java program is right? what conditions we need, what kind of expressions, arithmetic mumbo jumbo we need to get the desired output right? all you have to do is just write it down in simple English there are no syntax you have to worry about, no rules you have to worry about just simply write down the solution in your brain into words and viola you have pseudocode.
What is pseudocode?
Pseudocode is a simplified, informal way of writing algorithms in a form that resembles programming language, but without the strict syntax and semantics of a real programming language.
Logical constructs / Control Structure
So, remember how I said earlier that what we are doing with software is writing step by step instructions for computers to act out? Right? And then we said what we are doing is coming up with an algorithm to solve those problems, and that algorithm is the step by step guide.
Okay so what that means is this. Computers are dumb Everything they have to do, we have to point our finger and tell them like a toddler that’s why we say step by step instructions.
And the way computers read these instructions are literally step by step. they read line by line what we write. what that means is, until one instruction is done the next wont be executed. though it wont matter, there are hundreds of nano seconds of delay between lines of code being executed.
this means that these instructions are read in linear, or we call them Sequential Do you know what a sequence is? A sequence means, following one after the other; succession. So instructions are read like a waterfall, there are no going back up. Water just simply falls down and that’s it. Thats what a Sequential control structure means
Sequential control structure
- Sequence is a linear progression where one task is performed sequentially after another.
- Solution steps must follow each other in a logical sequence
- Statements are executed in the same order as they are written
Then there’s Selection; what does that mean? So from the name we can get, okay it has a selection. That means, when the program is coming do this, it has to make a choice. And the cannot go back in that choice. Imagine a T road, either you go left, or right. Thats what a Selection means, a choice the program makes.
A Iteration means, Well what do you mean by iteration? Iteration means doing something again and again, like repeating something or looping something. So in iterations, The program does something repeatedly, it can go back in itself until it choses to exit.
Now that we have an understanding of what goes under the software and the basic foundation of programming, now comes the fun/ or dreadful part, depending how you view it. Actually writing code.

me too buddy, me too. Let’s do it for the plot.
Now I am not going to explain every slide of the IP module, you can read the theory parts in the slides. I’ll only teach how to code. So, you should go check out the evolution of programming languages and then come back.
Programming: Pick your poison
Programming is a way of communicating with computers like we talked about earlier right? So, like in real life, there are hundreds of languages we use to communicate with each other. Like English, Chinese, Thai, Portuguese, Dutch and so on. Like that, there are hundreds of programming languages, (guess why they are called languages?) All you have to do is pick your poison depending on your needs. Like, if you want to make an android app, you’ll have to use Kotlin, or Dart If you want to make a web application, you’ll have to use Javascript (Svelte, React, Next…), PHP Desktop apps could be C++, C# or Java Games are written in C++, C# you get the idea.
Now Java, is a popular and old language. (notoriously hated for its syntax btw. Don’t tell them I said that)
 Check out more desired languages here
Check out more desired languages here

Anyways, We chose JAVA. Lets get this over with. (did you know the most played game minecraft is written entirely in java, which has over 1 million players even right now?)

JAVA
Alright, Let’s do this. First of all we are going to agree on 2 things. If you want to pass, you are going to remember these what are these?
- Keywords. (I can tell you what needs to be done, but if you don’t remember what to use then I can’t do much)
- Syntax Then we are going to agree that sometimes, some keywords, about them; don’t ask how those keywords work. I can tell you, but it’s not needed for you to get through it. Its like remembering sky is blue because its blue, and rain falls because sky is dark, nothing more to think much about.

Alright. Lessen number one.
Syntax
Alright, since from earlier, I threw this word around. What is syntax? in a normal language, syntax the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language.
So what is syntax is programming?
the syntax of a computer language is the rules that define the combinations of symbols that are considered to be correctly structured statements or expressions in that language
All you have to remember is, these are programming writing rules, like grammar for English, if you don’t use proper grammar, the sentences doesn’t make sense and the program crashes.
Structure of JAVA
So java is an object oriented language, we call it OOP, its not taught to us so I’m not going to explain in detail.
But the idea is;
OOP is built around a concept called classes.
A class is considered a mold, and the object is a copy of that mold.
For an example. Fruit is a class. Apples, oranges, and grapes are objects.
Don’t get it? don’t worry about it.
Why I briefed over it because, what we write code is inside a class.
that’s why at the top its called public class ....
now why we use public is a whole different thing, dont mind too much, like I said earlier its magic, it works somehow.
So here’s how you write a Java program.
// The file extension for a java program is .java
public class Main {
// this is your file name. in this case Main.java.
// Also, capitalization matters!
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Why we use this line? magic.
// it is needed okay? don't think much. it just works.
...
// This is where you write your code.
// What we are inside is called a METHOD.
}
}What to Remember
- Drill into your head the above skeleton, that is needed for any java program.
- Your class name should be the same as your file name, to the dot.
- String is capitalized inside the
main() - curly brackets are
{}mandatory. - Keep in mind about the indentations. (in notepad, press tab)
Basic outputs
Okay now that we know that, how do we make it do something? if we need to know something is working, it needs to do something that shows right? so, how do we figure out a program is doing something? well it needs to output. So how do we output in java.
KEYWORD: System.out.print or System.out.println
What is the difference?
System.out.print is used when you want to do like.
print AAAAA
print BBBBB
output:
AAAAA BBBBBSystem.out.println means, print a new line at the end of the output.
print AAAA
print BBBB
output:
AAAA
BBBBsee? alright. How do we do it in java?
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}System.out.println() is a function. So, it needs an argument. Don’t think much about it.
What it means for you is, it needs something within the brackets. A string, or a variable. Something that the function can output.
in this case a String.
How did we identify that?
any string is within two quotes " "
I’ll explain what are strings later.
What to remember
System.out.printlnandSystem.out.printare used to output anything into the command line.- “S” in
System.must always be capitalized. - The line must always end with a
;at the end. - You must pass something within the brackets, this is what will be printed.
Variables.
Hanging in there so far? good. Let’s crack on, we haven’t even touched the surface yet.
So what are variables? A variable is like a container that holds information for us to use in a program. Just like how we use different containers to hold different things (like a water bottle for water or a box for toys), we use variables to hold different types of information like numbers or words in programming.
You can also think of a variable as a label we stick on something, so we can refer to it easily later.
For example, if you want to remember someone’s age, you can create a variable called age and store their age in it.
Now, in actuality what happens is we are telling the program to go to the computer memory and hold onto a space in it so we can store some data onto it that we need to quickly access when the program is running.
For this, we have to tell the program how much space we need, thats why we have to say what type of data we are storing, because depending on the type the needed space might be larger or smaller.
This is what we call a variable deceleration. Here are the rules of variable deceleration in Java.
- type of variable
- name of the variable
- assign symbol
- value
- semicolon
Let’s say we want to store a person’s age in a program. We can do this with a variable. In Java, it looks like this:
int age = 25;So there are 4 things you have to understand.
intthis is the type of variable we are declaringageis the name of the variable we are declaring, this can be anything. thought there are some rules, I’ll explain them later.=Now a lot of you misunderstand this. I want you to forget your mathematical thinking. this is NOT equals. This keyword means simply IS. What does it mean? IS25this is the value we are assigning to the variableage
How do we read a variable? from right to left what? So how do we read the above? 25 is assigned to age as a integer in another way. age is 25
Variables
A variable is a named storage location in a program that holds data which can be changed or used later. Each variable has a data type that defines what kind of information it can store, such as numbers, text, or boolean values (true/false). Variables allow programmers to store and manipulate data throughout the execution of the program
Do we have an understanding now? good.
Rules of Variable Naming
- Variable names must be unique.
- Variable names can contain letters, digits and the underscore only.
- Variable names must start with a letter
- Variable names are case sensitive, num and Num are considered two different variables.
- Variable names cannot contain reserved keywords.
int name = 10; // name with simple characters
int _name = 20; // name with underscore at the begining
int name_two = 30; // name with underscore at the middle
int nameTwo_ = 40; // name with underscore at the end
int nameWith10 = 50; // name with number at the end
int name20WithNumber = 60; // name with number at the middleall above are valid names. The below are NOT VALID.
int 9name = 11; // its not valid; a number is at the start, see the two colors?
int if = 12; // the name contains a keyword see how its different in color?So, how to declare a variable. there are multiple ways.
// 1. Simple declaration
int number = 10;
// 2. type first, value later.
int numberTwo;
numberTwo = 20;
// 3. both together.
int numberThree, numberFour = 40;// <- for this all variables must be same type.
numberThree = 30;Common industry standards
- Write meaningful names.
- instead of writing
xuseage, ornumber
- When writing longer names, use camel case
- instead of
ageofplayeruseageOfPlayerfor better readability
Alright, what are the types of variables?
| Type | Syntax | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integer | int | Any number without a decimal point or a fraction, Any whole number | 1,10,20,500 |
| Float | float | Any number with a single precision decimal point | 10.2, 24.6 |
| Double | double | Any number with multiple decimal points with 16 decimal point precision | 1.2553, 3.97423 |
| Character | char | A single character, letter | ’A’, ‘b’,’@‘ |
| Strings | String | A collection of letters, characters / a written sentence like a word or a paragraph | ”Hello world”, “This is Java” |
| Boolean | bool | A true or false, on or off | True, False |
| Arrays | type[] | a collection of data (more on them later) | int[],String[] |
| How do we declare each of these? |
// remember the rule
// type name = value;
int number = 10; // integer is a whole value
float decimalNumber = 11.5; // a single decimal point
double numberPi = 3.1415926; // multiple decimal points
char singleCharacter = 'A'; // a single character. Use single quotes
String longWord = "Hello world" // a sentence, Use double quotesWhat to remember
- How to declare a variable
- what is a variable
- types of variables and their syntax
=this is not equals sign, but assignment operator. it means “is”- rules of variable naming.
Operators
Now that we understand what variables are what comes next is how do we modify these variables as we wish inside the ‘process’. That is when we use operators. Operators are like built in small functions inside a programming language.
All you have to understand is that, A computer is a glorified calculator. So everything we need is done by some mathematical bullshittery. For that there are multiple operators.
- Arithmetic operators. (we are familiar with this one, the every day maths stuff like + symbol and stuff)
- Relational Operators (these are what we used to compare stuff)
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Increment Operators
- Casting
This is going to be painful

1. Arithmetic Operators:
| Name | Syntax | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | + | Adds two values together | int sum = 5 + 3; (Result: sum = 8) |
| Subtraction | - | Subtracts the second value from the first | int diff = 10 - 4; (Result: diff = 6) |
| Multiplication | * | Multiplies two values | int prod = 6 * 7; (Result: prod = 42) |
| Division | / | Divides the first value by the second | int quotient = 10 / 2; (Result: quotient = 5) |
| Modulus (Remainder) | % | Returns the remainder of a division | int remainder = 10 % 3; (Result: remainder = 1) |
| Increment | ++ | Increases a value by 1 | int a = 5; a++; (Result: a = 6) |
| Decrement | -- | Decreases a value by 1 | int b = 5; b--; (Result: b = 4) |
Alright So all above look self explanatory no? The only confusing thing might be the remainder division because its new. But all you have to remember about that one is… let me draw you

Also, normal division returns the rounded up value. Also, there’s like order of how these things happen. Its called BODMAS
- Brackets
() - Power of
^ - Division
/&% - Multiplication
* - Addition
+ - Subtraction
-
2. Relational Operators:
| Name | Syntax | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equal to | == | Checks if two values are equal | if (a == b) (Checks if a equals b) |
| Not Equal to | != | Checks if two values are not equal | if (a != b) (Checks if a is not equal to b) |
| Greater than | > | Checks if the first value is greater than the second | if (a > b) (Checks if a is greater than b) |
| Less than | < | Checks if the first value is less than the second | if (a < b) (Checks if a is less than b) |
| Greater than or Equal to | >= | Checks if the first value is greater than or equal to the second | if (a >= b) (Checks if a is greater than or equal to b) |
| Less than or Equal to | <= | Checks if the first value is less than or equal to the second | if (a <= b) (Checks if a is less than or equal to b) |
Well, these are the things we use in maths to check some conditions right? that’s the same way we use them in programming what you have to remember is these “conditions” returns a boolean value, not a integer or other stuff that’s why they are written in if conditions.
3. Logical Operators:
| Name | Syntax | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logical AND | && | Returns true if both conditions are true | if (a > 0 && b > 0) (True if both a and b are greater than 0) |
| Logical OR | || | Returns true if at least one condition is true | if (a > 0 || b > 0) (True if either a or b is greater than 0) |
| Logical NOT | ! | Reverses the logical state of the operand | if (!isTrue) (True if isTrue is false) |
Like earlier these are used mostly in conditions. Just remember And means Multiply (so if one is 0 / false, both false) Or means Addition (so if one is 1 / true, then the output is true) Not means the opposite of whatever is the incoming, if the incoming is true then this makes it false and vise versa.
4. Assignment Operators:
| Name | Syntax | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assignment Operator | = | Assigns the value on the right to the variable on the left | int a = 5; (Assigns 5 to a) |
| Add and Assign | += | Adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result | a += 3; (Equivalent to a = a + 3) |
| Subtract and Assign | -= | Subtracts the right operand from the left and assigns the result | a -= 2; (Equivalent to a = a - 2) |
| Multiply and Assign | *= | Multiplies the left operand by the right and assigns the result | a *= 4; (Equivalent to a = a * 4) |
| Divide and Assign | /= | /= | Divides the left operand by the right and assigns the result | a /= 2; (Equivalent to a = a / 2) |
| Modulus and Assign | %= | Takes the modulus using both operands and assigns the result | a %= 3; (Equivalent to a = a % 3) |
| Below are not needed but purely for aesthetics | |||
| Bitwise AND and Assign | &= | &= | Performs a bitwise AND on both operands and assigns the result | a &= 2; (Equivalent to a = a & 2) |
| Bitwise OR and Assign | ||= | Performs a bitwise OR on both operands and assigns the result | a || = 3; (Equivalent to a = a || 3) |
| Bitwise XOR and Assign | ^= | ^= | Performs a bitwise XOR on both operands and assigns the result | a ^= 2; (Equivalent to a = a ^ 2) |
| Left Shift and Assign | <<= | <⇐ | Shifts the bits of the left operand to the left by a specified number and assigns the result | a <<= 2; (Equivalent to a = a << 2) |
| Right Shift and Assign | >>= | >>= | Shifts the bits of the left operand to the right by a specified number and assigns the result | a >>= 2; (Equivalent to a = a >> 2) |
The above are shorthand methods to write when youre messing with the same variable. if you feel like they are confusing, just forget about them.
You only have to remember is,
whatever is before the variable is done to the same variable.
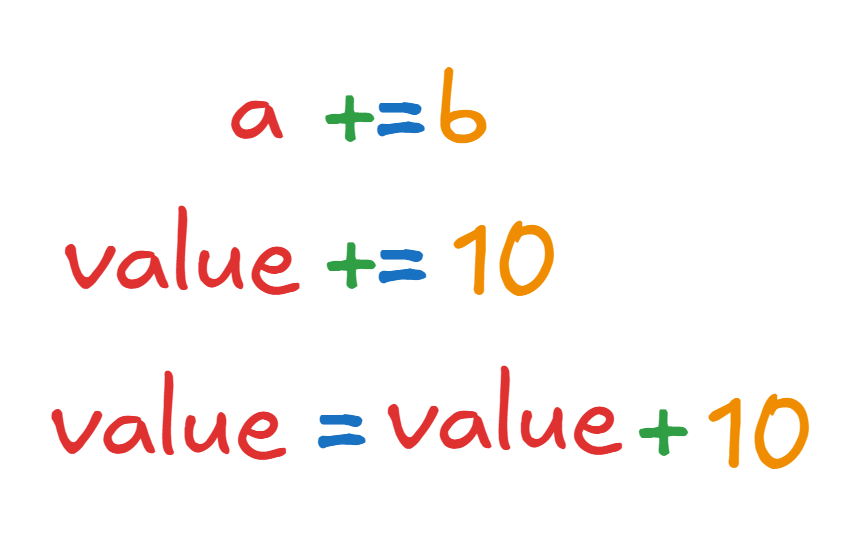 One rule of programming is never repeat yourself,
see how that is done here?
since you’ll be writing the same thing twice, here you use these shorthand to shorten your lines.
One rule of programming is never repeat yourself,
see how that is done here?
since you’ll be writing the same thing twice, here you use these shorthand to shorten your lines.
5. Increment Operators
Now there are mainly 2 operators.
- Increment
- Decrement
What these two are used for is, adding or subtracting 1 from any numerical value. Mainly they are used in loops. And each increment or decrement operator have 2 variants. They are Prefix and Postfix. Do you know what these two means? Prefix means, something before. Post means, something after.

So what does this mean? In prefix, whatever happens, happens first before coming to the next word. in Postfix the name comes first before whatever happens. I’ll explain it. So; In increment, we have two variants
- prefix
++num - postfix
num++
So how do they work?
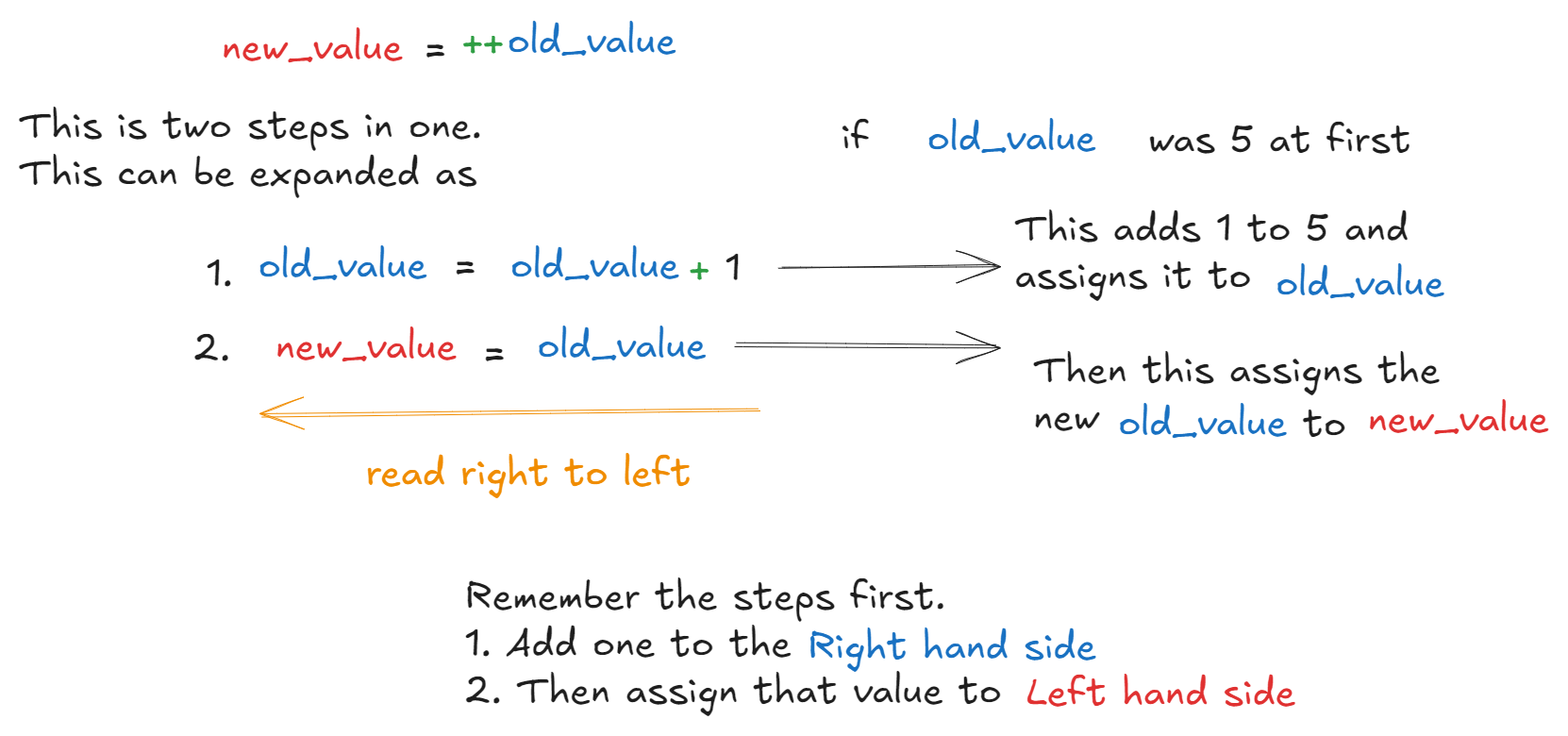
If we check the outputs
int old_value = 5;
int new_value = ++old_value;
System.out.print(old_value); //outputs 6
System.out.print(new_value); // outputs 6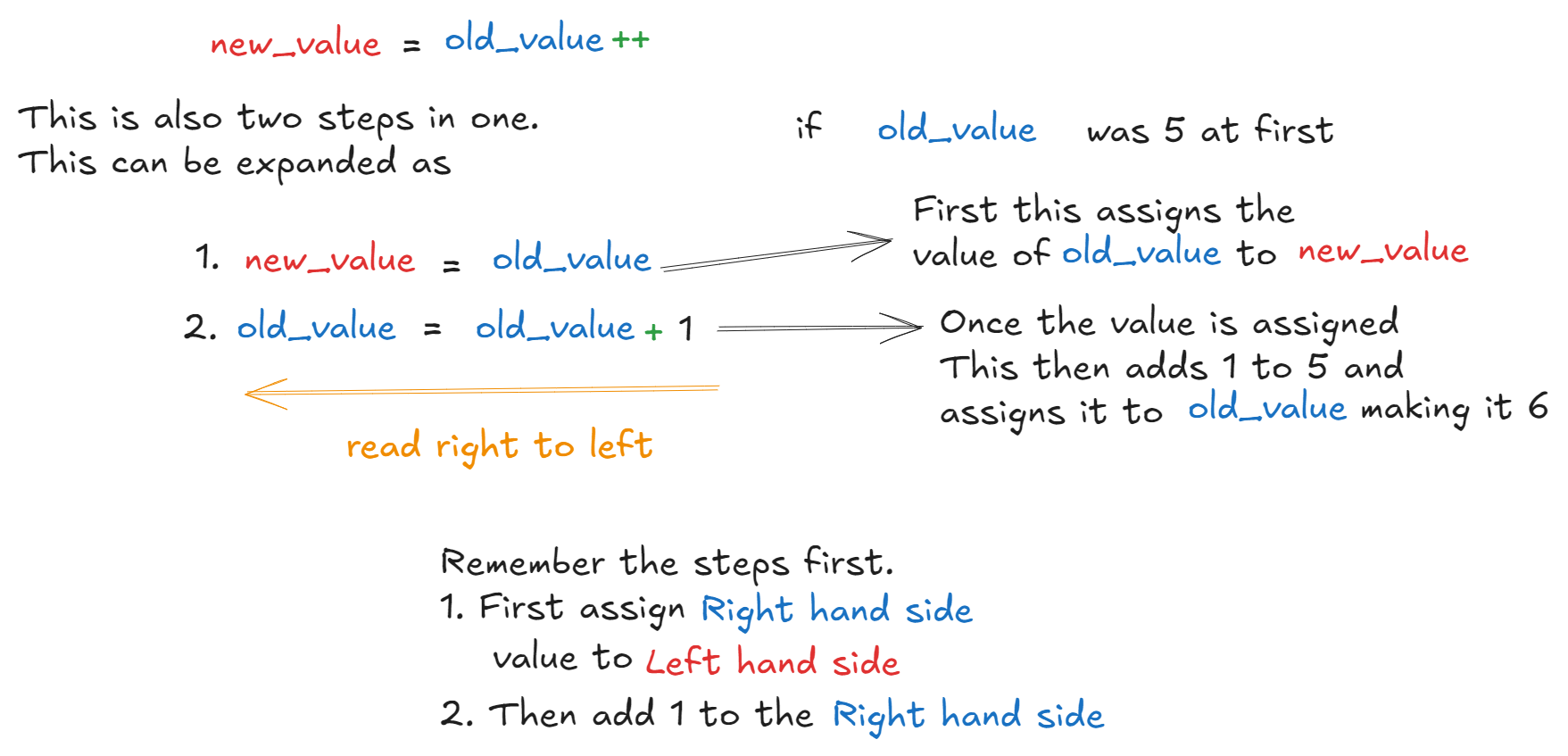
int old_value = 5;
int new_value = old_value++;
System.out.print(old_value); //outputs 6
System.out.print(new_value); // outputs 5Like this, the decrement is the same.
int old_value = 10;
int new_value = --old_value;
System.out.print(old_value); //outputs 9
System.out.print(new_value); // outputs 9
// ---POSTFIX---
int old_value = 10;
int new_value = old_value--;
System.out.print(old_value); //outputs 9
System.out.print(new_value); // outputs 10kapeesh? good.
6. Casting
So, casting is commonly referred to as “type casting” and what can we gather by that? we know what a type is right? its when we tell the program what type of variable we are using. Alright So type casting in programming is like converting one type of data into another type in programming. Think of it as changing the shape of something to make it fit into a different container.
For example, in real life, if you want to pour juice from a large bottle into a small glass, you can do it, but some juice might spill. In programming, when you convert (cast) a bigger type of data (like a double) into a smaller one (like an int), you might lose some information, but it’s still possible.
Let’s say you have a decimal number, but you want to store it as a whole number. You can cast it:
double decimalNumber = 9.99;
int wholeNumber = (int) decimalNumber; // Casting double to intHere, decimalNumber was 9.99, but when you cast it to an int, it becomes 9, dropping the decimal part.
There are two types of Casting:
- Implicit Casting (Automatic Casting):
- So this happens automatically when converting a smaller type to a bigger type because there’s no risk of losing information.
int smallNumber = 10;
double bigNumber = smallNumber; // Automatically converts int to double- Explicit Casting (Manual Casting):
- Here, you need to manually, specifically tell the program what your converting. this happens when converting a bigger type into a smaller type because you might lose some data.
double decimalValue = 12.5;
int wholeValue = (int) decimalValue; // You manually cast double to intWhat to remember
- Casting means converting one type of data into another.
- Implicit casting happens automatically (e.g., int to double).
- Explicit casting must be done manually (e.g., double to int) to avoid data loss.
- You have to use
(type)valueto do the casting.
Now you have the groundwork to finally start programming. Jeez we haven’t even started programming yet.

Dramatic much? Please. We’ll get there.
